
Maria Consiglia Rasulo
 IREA participates in the XXVI edition of Futuro Remoto, a great event of science, culture and entertainment, that will be held in Città della Scienza in Naples from October 4 to November 4, 2012. This year's event, titled "The factories of heaven," is devoted entirely to space, a theme dear to IREA researchers working in the field of Remote Sensing who study innovative methodologies and techniques for acquisition, processing and interpretation of remotely sensed data.
IREA participates in the XXVI edition of Futuro Remoto, a great event of science, culture and entertainment, that will be held in Città della Scienza in Naples from October 4 to November 4, 2012. This year's event, titled "The factories of heaven," is devoted entirely to space, a theme dear to IREA researchers working in the field of Remote Sensing who study innovative methodologies and techniques for acquisition, processing and interpretation of remotely sensed data.
Wednesday, October 31 conference for schools
dr. Gianfranco Fornaro
The Earth controlled by radar "eyes"
 The next July 8, with the organizational and logistical support of IREA, it will be held the third annual day of SERIT, the national technology platform promoted by CNR and Finmeccanica which includes companies and institutions in Italy dealing with research in the field of security. The event will be an opportunity to present the third Volume of the SERIT Platform which includes national priorities to support in “Horizon 2020”.
The next July 8, with the organizational and logistical support of IREA, it will be held the third annual day of SERIT, the national technology platform promoted by CNR and Finmeccanica which includes companies and institutions in Italy dealing with research in the field of security. The event will be an opportunity to present the third Volume of the SERIT Platform which includes national priorities to support in “Horizon 2020”.
The day will begin with the greeting of the President of the National Research Council of Italy, the Mayor of Naples and the President of the Campania Region. Then, in the Round Table chaired by a representative of the European Commission, funding opportunities for the themes "Security in H2020", with particular reference to the role of research and industry in Southern Italy, will be discussed. In the afternoon there will be a brief presentation of IREA which, with the laboratory Radar for security applications and monitoring of the territory, won the Serit Award 2012, the recognition to the public and / or private Italian laboratory which stood out for the research and innovation in the field of Security.
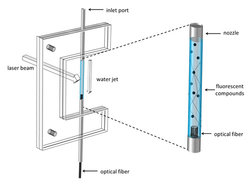 A naked jet of water that doubles as both the sample and the collection equipment, providing a simple, cheap, and portable new tool to analyze liquids. This is what a group of researchers of Irea, composed of Gianluca Persichetti and Genni Testa and led by Romeo Bernini, have designed and realized.
A naked jet of water that doubles as both the sample and the collection equipment, providing a simple, cheap, and portable new tool to analyze liquids. This is what a group of researchers of Irea, composed of Gianluca Persichetti and Genni Testa and led by Romeo Bernini, have designed and realized.
This is an optofluidic sensor that forgoes the channels in favor of a narrow stream of water unconfined by tubes or pipes. Typical microfluidic detectors for testing water are built to make use of the fluorescent property of pollutants and rely on narrow channels to hold and control the water samples with their fluorescing organic compounds. One of the major limitations of such devices is determined by the fact that laser light that illuminates bacteria and chemicals in the water also shines on the channel walls, where it scatters and obscures the distinction between the fluorescing contaminants and their background. The reliability of measurements made using these instruments is therefore weakened. Thanks to the new technique developed by researchers at IREA, water sample is pumped through a nozzle at 1.4 meters per second, producing a narrow stream that is less than a millimeter in diameter. When it is shined by UV laser, the fluorescent light produced by the pollutants and bacteria bounces around and is trapped inside the jet.
The researchers tested their device with varying amounts of some of the main pollutants of ground water which are hazardous and carcinogenic, finding that the device was extremely sensitive. It could detect pollutant levels even lower than those allowed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The instrument could also sense Bacillus subtillus, a harmless bacterium similar to the one that causes anthrax.
The device was developed in the framework of the research project ACQUASENSE. It does not require any pretreatment of the sample to be analyzed and can be easily plugged in normal water pipes. The extreme cheapness and compactness of the device make it suitable for its use in early warning systems for water quality monitoring.
The interest aroused by the research result is proved from having been selected for the news of the Optical Society of America (OSA).
 For the first time satellite data and ground measurements were used in order to detect the possible magma rising that 'announces' the eruptive activity of Etna. The study, result of collaboration between the National Research Council of Italy (CNR), the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (INGV) and the Italian Space Agency (ASI), was published in Scientific Reports of Nature. Understand the internal structure of a volcano and its functioning is one of the main target of volcanological studies. In order to do this, scientists can only be based on information gathered on the volcano surface and on the analysis products released (lava, gases, ash, ...). For the first time the study utilizes synergically the measurements of ground deflection, calculated by using data collected by satellite radars as Ers / Envisat and Cosmo-SkyMed, and information on the small variations in the gravitational field measured near the volcano surface.
For the first time satellite data and ground measurements were used in order to detect the possible magma rising that 'announces' the eruptive activity of Etna. The study, result of collaboration between the National Research Council of Italy (CNR), the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (INGV) and the Italian Space Agency (ASI), was published in Scientific Reports of Nature. Understand the internal structure of a volcano and its functioning is one of the main target of volcanological studies. In order to do this, scientists can only be based on information gathered on the volcano surface and on the analysis products released (lava, gases, ash, ...). For the first time the study utilizes synergically the measurements of ground deflection, calculated by using data collected by satellite radars as Ers / Envisat and Cosmo-SkyMed, and information on the small variations in the gravitational field measured near the volcano surface.
The sustainable city: scientific and technological innovation for efficient, safe and healthy cities
 As part of the events to celebrate the 90th anniversary of the National Research Council of Italy, the Department of Engineering, ICT and Technology for Energy and Transport (DIITET) organized on December 10, 2013 in Rome a conference entitled "The Sustainable City: scientific and technological innovation for efficient, healthy and safe cities". Purpose of the initiative was to present projects, methodologies, tools, developed by the Institutes afferent to DIITET, aimed at creating smart cities designed to improve life quality. During the day the journalist Daniele Cerrato – TV host of TGR Leonardo, interviewed some experts in the CNR. Among them Gianfranco Fornaro, senior researcher at IREA, who dealt with the theme of Global security for the city: technologies for satellite monitoring of urban areas and infrastructures.
As part of the events to celebrate the 90th anniversary of the National Research Council of Italy, the Department of Engineering, ICT and Technology for Energy and Transport (DIITET) organized on December 10, 2013 in Rome a conference entitled "The Sustainable City: scientific and technological innovation for efficient, healthy and safe cities". Purpose of the initiative was to present projects, methodologies, tools, developed by the Institutes afferent to DIITET, aimed at creating smart cities designed to improve life quality. During the day the journalist Daniele Cerrato – TV host of TGR Leonardo, interviewed some experts in the CNR. Among them Gianfranco Fornaro, senior researcher at IREA, who dealt with the theme of Global security for the city: technologies for satellite monitoring of urban areas and infrastructures.
During the XX Italian Meeting on Electromagnetics held in Padova from September 15 to 18, dr. Rosa Scapaticci, research fellow at IREA, together with Martina Bevacqua Ph.D. student at the University Mediterranea of Reggio Calabria, was honored with the Barzilai Prize, a prestigious award assigned by SIEm (Italian Society of Electromagnetics) to the best work proposed at the Meeting by authors under the age of 35 years.
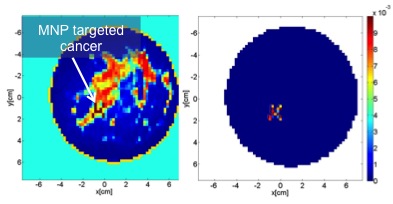
The award was assigned to the work 'Exploiting compressive sensing in Magnetic Nano Particle enhanced MWI for breast cancer imaging' in which the young scholars have proposed a processing methodology able to improve the performance of a new technique for microwave diagnostics of breast cancer, developed at the IREA within the project MERIT.
This diagnostic technique uses electromagnetic fields at microwave frequencies, as a non-invasive and non-harmful survey instrument, jointly with magnetic nanoparticles as contrast agent. These latter, "functionalized" through appropriate biochemical procedures, are indeed able to concentrate only in tumor tissues and to induce a selective variation of the magnetic properties. Given the non magnetic nature of human tissues, this "marking" allows to obtain a highly reliable diagnostic technique.
The methodology proposed by the authors, who analyzed its potentiality through a broad campaign of numerical simulations and found improved performances compared to the standard techniques used so far, can provide significant advantages such as the ability to identify small lesions, a crucial factor in the early diagnosis, or to appreciate the morphology of the lesion, useful information for clinicians in order to identify its typology.
“Space, a driver for competitiveness and growth”
27-28 February 2014 - Bari, Italy
NEREUS (Network of European Regions Using Space Technologies) and its member region Apulia organized an international conference aimed at presenting how space uses and applications respond to a number of societal and economic challenges of the everyday life. Bringing together the demand and supply side of space services, the idea is to better understand regional needs and potential benefits of an increased uptake.
The event, mainly addressed to European regions, local authorities and their stakeholders, featured interventions by representatives of the European Commission, Space Agencies as well as representatives from the academic, research and industrial sectors to share knowledge, experiences and expertise. Thematic and best practice sessions as well as round table debates animated the 2-day event.
During the Session Space for Environment& Sustainable Energy, IREA-CNR (Massimo Antoninetti) presented the Earth observation technologies to support agro sector in Lombardy, highlighting experiences and prospective to be acquired during two research projects, respectively sponsored in the frame of a special agreement between CNR and Lombardy Region (Space4agri), and by EC in the frame of Framework Programme 7 (ERMES).
During the Session Space for Transport & Infrastructures, IREA-CNR (Francesco Soldovieri) gave a talk on the outcomes and the perspectives of the project “Integrated System for Transport Infrastructures surveillance and Monitoring by Electromagnetic Sensing” (ISTIMES). funded in the Joint Call ICT-Security, 2007. The project had three years duration with the end on June 2012” ISTIMES regarding the integration of EO and ground based sensing technologies for the monitoring and quick damage assessment of the critical transport infrastructures. The project has been flagged as a “success case”, as “success/case story”, “High visibility/media attractive project” and having a “Substantial R&D breakthrough character” by European Commission.
IREA-CNR actively participates in NEREUS. IREA-CNR is an associated member of NEREUS, and leaded its flagship FP7 project DORIS_Net to set up the European network of Copernicus-GMES Regional Contact Offices (RCOs) to raise awareness and strengthen regional involvement in Copernicus-GMES, Europe’s flagship programme for Global Monitoring of the Environment and Security.
IDL (Interactive Data Language) routines implementing interferogram noise-filtering algorithm
The interferogram noise-filtering procedure permits to drastically mitigate the decorrelation noise artifacts affecting a sequence of time-redundant multi-look small baseline interferograms by properly exploiting their temporal relationships.
IDL (Interactive Data Language) routines implementing interferogram selection algorithm
The interferogram selection algorithm permits to identify an optimal network of time-redundant multi-look small baseline interferograms forming a reduced triangulation in the temporal/perpendicular baseline plane, by properly exploiting a Simulated Annealing searching strategy.
In order to download the IDL routines an authorization is required. Please contact dr. Antonio Pepe, at the following e-mail address This e-mail address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it , to ask for credentials (ID and password).

The challenge, organized by NASA and 333 partners around the world, including space agencies, research institutions and universities, was held on 20 and 21 of April, 2013 and involved about 9,000 people in 83 cities around the world. Aim of the event was producing solutions to the global needs relevant to life both on Earth and in space. The participants worked together for 48 hours, forming teams focused on solving a particular challenge. More than 770 solutions were proposed and then evaluated by a panel, consisting of representatives of NASA and other governmental and nongovernmental organizations, which chose the best solutions for different types of awards, by making criteria of judgment based on the impact, creativity, complexity, collaboration, product, sustainability and presentation of the team and its solution.
At the University of Rome 'La Sapienza' a team, made up young international people including Mr. Chandrakanta Ojha, participated to the KSC challenge under ‘Deployable Greenhouse’ with a project entitled ‘Green on the Red Planet’. Out of the 16 participating teams from Italy, the ‘Green on the Red Planet’ group obtained the first position as a local winner and achieved the 2nd place to the KSC global challenge as well.
The project concerns to the development of a modular greenhouse with rigid and inflatable elements for a self-sustainable future human base on Mars. It would be capable of providing quality and quantity of food for four astronauts during their stay on Mars and would be well equipped with automatic operating systems by exploiting energy system based on solar, wind and nuclear power to autonomous harvesting using robot farmers.
Bresciani M., Giardino C.
A validation exercise of ICOL applied to MERIS data of Lake Trasimeno
Boschetti M., Bresciani M., Giardino C.
Analisi delle funzioni ecosistemiche e delle caratteristiche ecologiche degli ambiti umidi perifluviali del Po mantovano e studio delle aree pilota interessate da interventi di ripristino funzionale ed ecologico
Giardino C., Bresciani M.
Analysis of a OCEANSAT-2 image for studying Italian inland waters
Carrara P.
EnvEurope: Environmental quality and pressures assessment across Europe
Bresciani M., Giardino C., Musanti M.
Field measurements supporting AISA image processing
Bresciani M., Carrara P., Giardino C., L'Astorina A., Lella S.
Geoportale della qualità dell'acqua del lago di Garda
Criscuolo L., Carrara P., Pepe M.
Geoportale dimostrativo dei prodotti dell'attivita' di ricerca dell'IREA UOS Milano
L'Astorina A., Paolucci P.
Information Architecture del sito web IREA
Bresciani M., Giardino C.
Monitoraggio dei canneti veronesi del lago di Garda 2010
Simone Lella
Portale per la diffusione dei dati sulla trasparenza e la temperatura del lago di Garda
L'Astorina A., Paolucci P.
User profile del sito web IREA



